The Science of the ATP PC System Recovery Timeline Graph
You approach the bar. You lift it for 3 reps. It feels easy. You rest for 30 seconds. You try to lift it again. You fail. Why? You did not get weaker in 30 seconds. Your muscles did not disappear. The problem is fuel. You ran out of gas.
Understanding the atp pc system recovery timeline graph is the first step in moving from “working out” to “training.” That gas is called Adenosine Triphosphate known as ATP.
Adenosine Triphosphate Replenishment Rate Per Minute
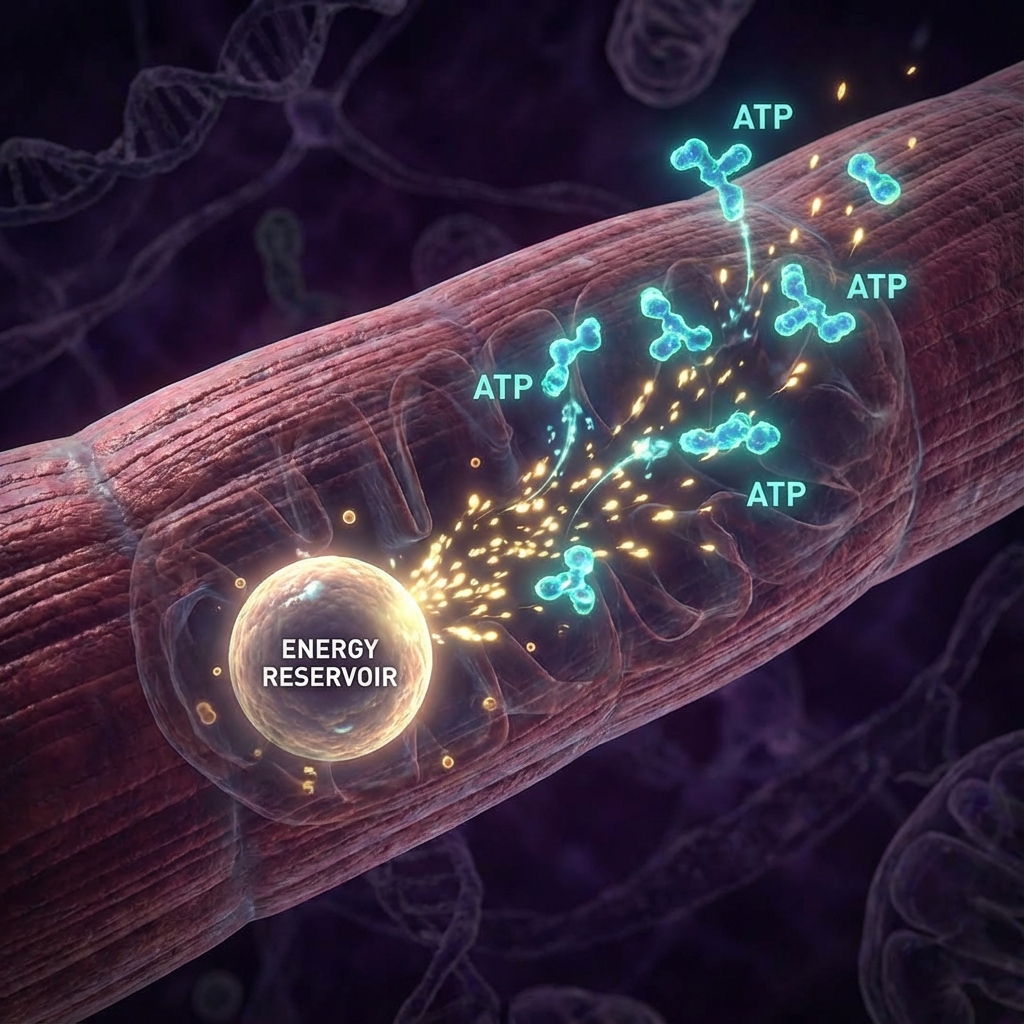
ATP is the currency of energy. For powerlifters, weightlifters, and sprinters, the ATP-PC system is king. It provides energy faster than any other system, but it has a tiny fuel tank. To perform another heavy set, you must refill the tank using Creatine Phosphate or PC.
This process allows for a predictable adenosine triphosphate replenishment rate per minute:
- 30 Seconds: ~50% Replenished, which is the half-life mark.
- 60 Seconds: ~75-85% Replenished.
- 180 Seconds or 3 Minutes: ~98-100% Replenished.
This is why “quick rests” destroy performance. If you rest for only 60 seconds, you are starting your next set with a significant fuel deficit. You are literally weaker than you were a minute ago.
For powerlifters, weightlifters, and sprinters, the ATP-PC system is king. It provides energy faster than any other system, but it has a tiny fuel tank.
The Depletion Curve
When you perform a maximal lift, you drain your ATP stores almost instantly. By the end of a heavy set of 5 reps, your tank is empty.
To perform another heavy set, you must refill the tank. This process relies on Creatine Phosphate also known as PC to donate a phosphate molecule to ADP, turning it back into ATP.
This recharge takes time.
The Science of Replenishment
Research has mapped this recovery curve precisely:
- 30 Seconds: ~50% Replenished
- 60 Seconds: ~75-85% Replenished
- 180 Seconds or 3 Minutes: ~98-100% Replenished
This is why “quick rests” destroy strength performance. If you rest for only 60 seconds, you are starting your next set with a 15% to 25% fuel deficit. You are literally weaker than you were a minute ago.
Why You Can’t “Push Through”
You cannot willpower your way through biochemistry.
If your ATP stores are low, your muscle fibers physically cannot slide across each other with the same force. No amount of “hype” or smelling salts can change this.
When you attempt a heavy lift without full ATP recovery, your body compensates. It recruits weaker, slower fibers to help. Form breaks down. The risk of injury skyrockets.
Practical Application
For strength athletes, the clock is your best training partner.
- For Strength of 1 to 5 reps: Rest 3 to 5 minutes. You need 100% of your ATP.
- For Hypertrophy of 8 to 12 reps: Rest 90 seconds to 2 minutes. It is okay to start with slightly depleted ATP to induce metabolic stress.
- For Endurance of 15 or more reps: Rest 30 to 60 seconds. You are training the body to function under fatigue.
Visualizing the Invisible
You cannot see your ATP levels. But we can model them.
Our Rest Timer uses the mathematical half-life of Phosphocreatine resynthesis to show you a live graph of your estimated energy levels.
When the bar turns green, your tank is full. Lift heavy. Lift safe.